Production Technology
Shandong Dabo Pump Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Boshan District, Zibo, Shandong, China
Selection of AAC slurry transfer pumps
Loading...Slurry pumps are commonly and very frequently used in the AAC industry. The proper selection of slurry pumps is not only related to the aspects of investment, energy consumption and production efficiency, but also to the maintenance load and overall performance of the production line. Therefore, slurry pumps are not only required to provide high investment efficiency and production efficiency, but also stable performance characteristics and high durability.
Application scenarios for slurry pumps
Slurry pumps are mainly used in the mortar or fly ash slurry preparation section, slurry storage section, casting section, and cutting section. In addition, they are also commonly used for the condensate water and flushing water in the autoclave, since these contain a certain amount of solid siliceous powder. When the production line is scattered due to site restrictions, slurry pumps are used for long-distance connection.
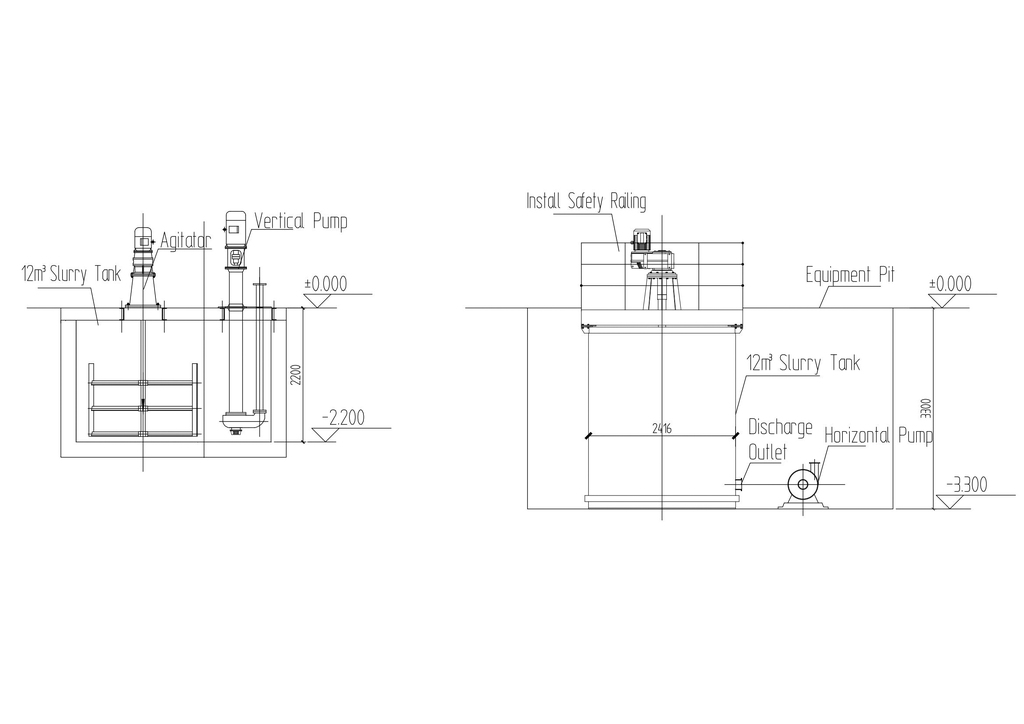
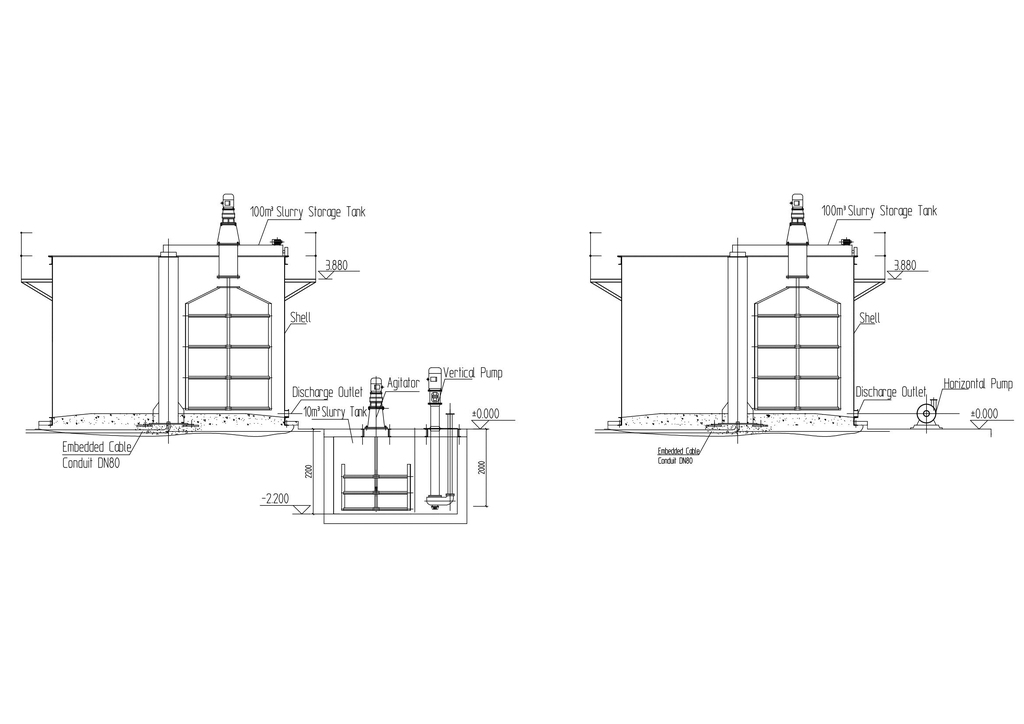
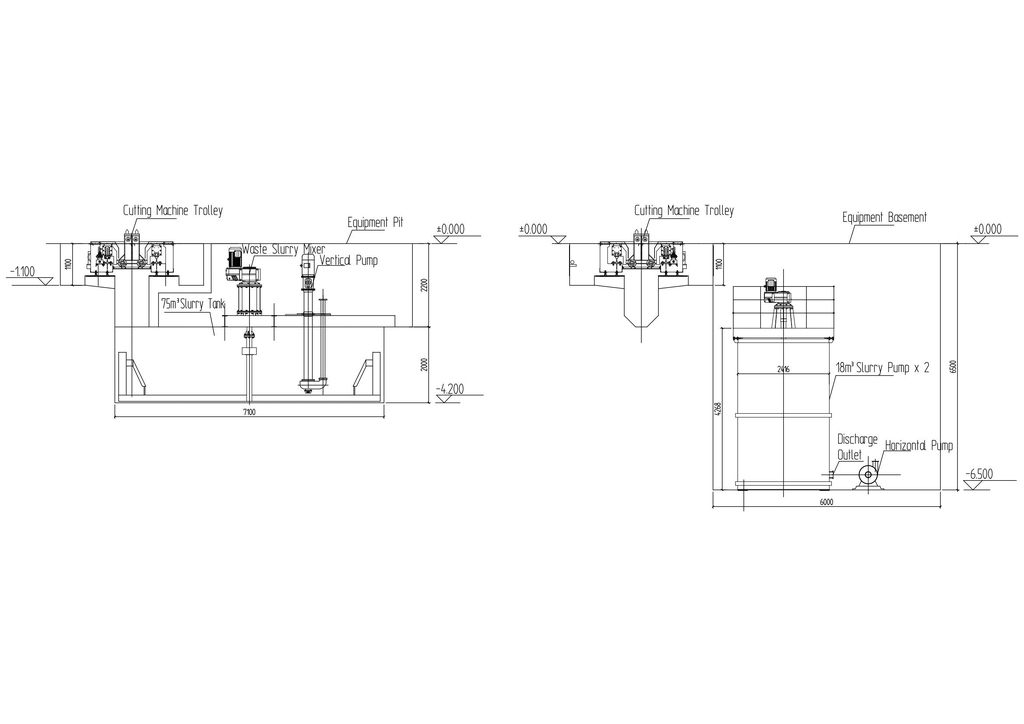
In the slurry storage section, when the slurry pump is equipped for the downward flow of the slurry storage tank, i.e. when the slurry storage tank is arranged above ground level, either a horizontal pump or a vertical pump can be used. When using a vertical pump, a transition tank needs to be set up, while the layout of a horizontal pump is relatively simple. Therefore, horizontal pumps are commonly used abroad (Fig. 2 b), while vertical pumps are mostly used in China (Fig. 2 a). Both types of pumps are applicable to the waste slurry tank at the bottom of the cutting machine. Since the waste slurry tank is positioned at a relatively deep level, it must be installed at the bottom elevation of the waste slurry tank, generally around - 6.000 m, if a horizontal pump is used. This poses a challenge to both construction projects and equipment maintenance. Some production lines still use horizontal pumps for transportation in the waste slurry tank under the cutting machine to match the overall functions of the unit (Fig. 3 b). However, in recent years, vertical pumps have increasingly been used for transportation (Fig. 3 a).
For the casting section, the autoclave curing section, and the transportation of wastewater from flushing, the layout generally follows the form of the slurry preparation section. When it comes to long-distance transportation, the main considerations are the transportation distance and the head, and the layout can also refer to that of the slurry preparation section.
Regardless of the work position where they are used, the application scenarios for slurry pumps in the AAC industry can be summarized into the following three categories: transportation in the raw material preparation section (Fig. 1), transportation in the slurry storage section (Fig. 2), and transportation in the cutting section (Fig. 3).
Selection of slurry transfer pumps
Operating conditions of slurry pumps
Slurry pumps account for a relatively small proportion in the total investment of the production line. However, they are frequently in use and have a significant impact on the daily operation and functionality of the production line. Therefore, when selecting slurry pumps, less consideration is given to the equipment purchase cost, and more emphasis is placed on the operational stability of the equipment and the convenience that comes with low maintenance.
Thus, for the transportation of slurry in the slurry preparation section, the casting section, the cutting section, the autoclave curing section, and the conveyance of wastewater from the flushing process, vertical pumps are chosen preferentially. This is because sunken-type slurry tanks are installed to collect the slurry and wastewater, giving vertical pumps a natural advantage. In the slurry storage section, since the storage tanks are set above ground level, relatively speaking, using horizontal pumps is a both simple and clean solution.
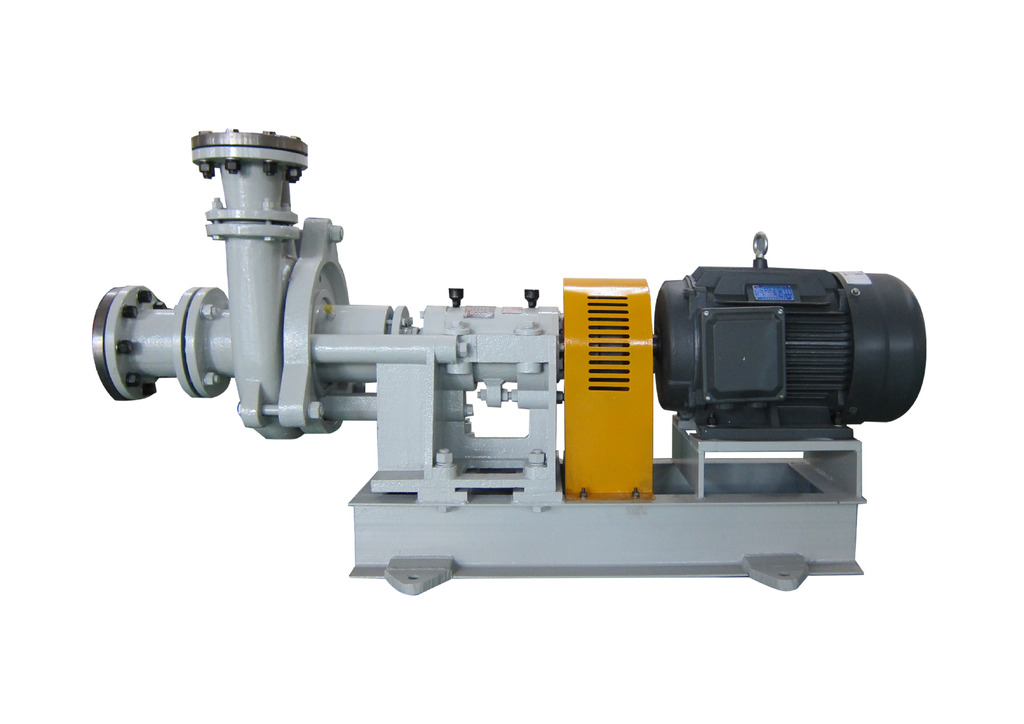
In the past, horizontal pumps were more commonly selected abroad. Firstly, the quality of foreign horizontal pumps was stable. Secondly, slurry transportation abroad mostly adopted a continuous mode, which caused relatively little problems when using horizontal pumps. Thirdly, horizontal pumps were used for enclosed transportation, providing a better working environment.
As mentioned above, using a horizontal pump in the slurry storage section is the optimal choice (Fig. 2 b). When using a horizontal pump in the slurry preparation section (or similar application scenarios), a sunken working surface must be constructed, which increases the civil construction cost. Moreover, it is not conducive to maintenance, safety, and hygiene (Fig. 1 b). When using a horizontal pump in the cutting section, since the waste slurry tank of the cutting machine is already below - 2.500 m, and when equipped with a slurry tank with a height of about 4 m, the installation surface of the pump will reach - 6.500 m or even lower. For example, in the original Hebel and Weihan Type I, the waste slurry transfer pumps were installed in the basement on the second underground floor. Obviously, the foundation construction cost is relatively high, and the position of the pump is very unfavorable for maintenance, safety, and hygiene. However, considering the unity of equipment configuration, this practice remained popular for a long time.
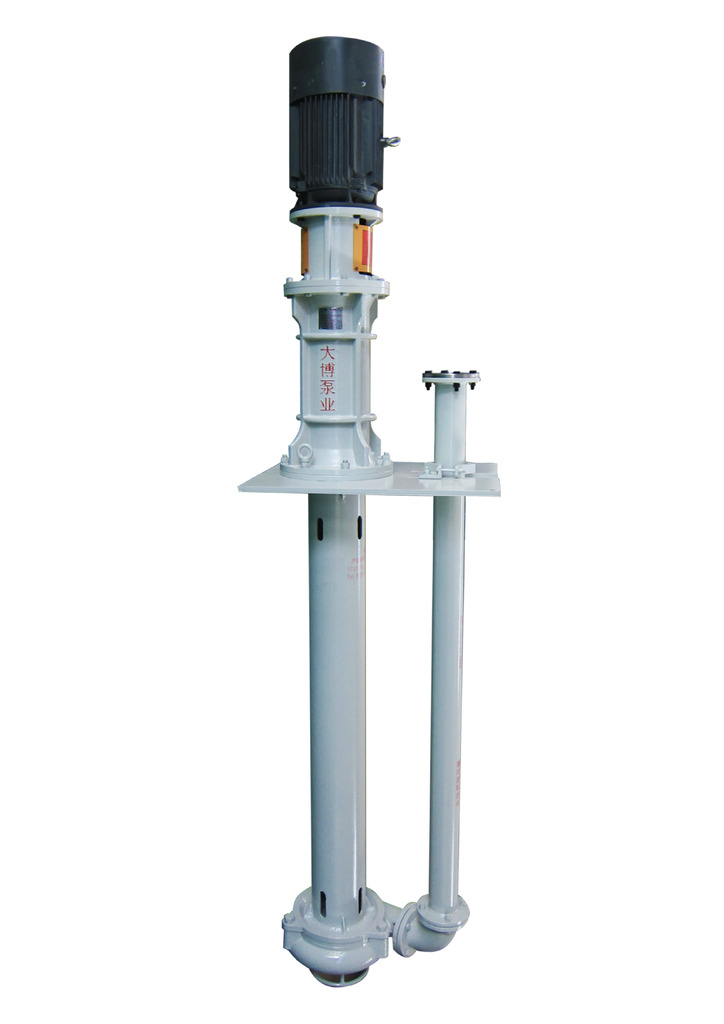
In China, vertical pumps are more commonly used, mainly because the process predominantly adopts intermittent transportation and because more considerations are given to investment and maintenance. Although components of vertical pumps wear out relatively quickly, using mud pumps can still assist in meeting the requirements, albeit with relatively high efforts related to renewal and maintenance work. If a horizontal pump is used, intermittent operation will cause significant damage to the pump. Even if continuous transportation is adopted, if the flushing is not thorough when the pump stops, the pump may be damaged. Moreover, the only scenario where a horizontal pump is applicable is the slurry storage section. In accordance with the requirements of equipment configuration consistency, vertical pumps have gradually been adopted in China.
In recent years, the suspended shaft vertical slurry pump has been developed. Since its drive and support system are not situated below the material level, the pump's service life and operational stability have been significantly improved, and the maintenance requirements have been greatly reduced. As a result, its application is expanding continuously.
Slurry pump performance analysis
The performance of slurry pumps can be compared in terms of power, efficiency, and failure rate under the same flow rate, head, and caliber conditions. A comparison of several pumps with a flow rate Q = 90 m³/h, a head H = 25 m and outlet diameter ND = 100 mm is presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Comparison of slurry pump performance characteristics.
Name and model and rated parameters | Power(kW) | Efficiency(%) | Failure rate(%) | Operating life of impeller(m3/h) | Weight(kg) | ||
Name | Flow rate/head | Outlet pipe diameter/submerged depth | |||||
Vertical mud pump | 80-100/15-17 | 100/1,940 | 15 | 61 | 5.0 | 3,500/158 | 270 |
Vertical slurry pump | 74-293/5.5-37 | 100/-- | 15-45 | 65.8 | 1.0 | 155,520/3,375 | 640 |
Suspended shaft vertical pump | 91/25.4 | 120/2,100 | 18.5 | 52.5 | 0.5 | 256,608/5,568 | 950 |
Horizontal slurry pump | 41-167/8.9-47 | 80 | 37 | 62.4 | 2.0 | 155,520/3,375 | 480 |
Horizontal slurry pump | 120/25 | 80 | 22 | 66 | 2.0 | 155,520/3,375 | 500 |
The service life of the impeller is calculated according to the output of AAC (m³) and the running time (h, including the interval time). | |||||||
Table 1 shows that due to different applications and manufacturers, the technical parameters of different slurry pumps vary to some extent. However, from the perspective of production applicability in the AAC industry, among vertical pumps, mud pumps are inferior to slurry pumps, and slurry pumps are inferior to suspended shaft pumps. When comparing vertical pumps with horizontal pumps, vertical pumps are obviously superior to horizontal pumps, with the exception that the performance of mud pumps is seriously unsuitable. Once a vertical pump has stopped, the slurry automatically returns to the slurry tank and will not deposit in the pump body, thus causing no damage to the pump body. Different structures of vertical pumps have a significant impact on service life and failure rate. The impeller support of a mud pump is situated below the material level. This structure works well for water or mud with a relatively low density, but for the slurry in the AAC industry, which usually has a density greater than 1.38 g/cm³, it is clearly not suitable. Although the slurry pump improves the wear-resistance of the flow-through components, the wear problem has not been fundamentally solved. For the suspended shaft slurry pump, since the transmission support of the shaft is not situated below the liquid level, damage from the working medium is avoided, the failure rate is reduced, and the service life is increased. Although horizontal pumps require flushing with clean water after operation, some sediment always remains. If the operator is negligent, the sediment will increase significantly, causing malfunctions of the horizontal pump. Due to the relatively high operating load and high start-stop frequency, the failure rate will increase considerably.
Safety and hygiene of the slurry pump working environment
Slurry pumps generally do not have exposed transmission parts, and there is usually no high-pressure or fire hazard. The hygiene issues of slurry pumps mainly stem from leakage and splashing. Leakage predominantly occurs in horizontal pumps when improper operation, maintenance, and servicing lead to the failure of the seal in the transmission part. In contrast, vertical pumps have no sealing problems. When the vertical pump stops, the slurry flows back to the slurry tank, preventing sedimentation and blockages, which could cause leakage. Eliminating the splashing during the stirring of the slurry tank improves the working environment associated with a vertical pump, in comparison to a horizontal pump. However, if a high-quality horizontal pump is used, and its seal does not leak and it is properly operated and maintained, the working environment of a horizontal pump will be cleaner than that of a vertical pump, as the horizontal pump operates in a fully enclosed manner.


Summary
Based on the above-mentioned analysis of the AAC industry, when considering only applicability and stability, the optimal production configuration includes the use vertical pumps for the raw material preparation section, the casting section, the cutting section, the transportation of autoclave wastewater, the flushing of wastewater, and for long-distance connections. In particular, the suspended shaft vertical slurry pump is highly recommended. This type of pump is specifically designed for the AAC industry, with a failure rate of only 0.5%. Especially in the cutting section, it has obvious advantages in reducing investment costs and facilitating maintenance.
Regarding the slurry storage section, in terms of performance, horizontal pumps might be considered suitable. However, it needs to be considered that horizontal pumps require a relatively high degree of operation and maintenance, and that any operational or maintenance errors can have a significant impact on production and the environment. Taking into account the requirement for equipment configuration consistency, it is better to use the suspended shaft vertical slurry pump instead.
Advantages of vertical slurry pumps
There may be several reasons for selecting vertical slurry pumps:
· Installation method: The installation of vertical pumps is more cost-effective than that of horizontal pumps.
· Sealing feature: Horizontal pumps require sealing, while vertical pumps don not require sealing. Without a seal, there are no leakage points.
· Behavior when the pump stops: When the pump stops, the slurry in the pipeline of a horizontal pump will flow back into the pump cavity. After a while, it may cause blockage. However, the slurry in a vertical pump will flow back into the tank through the open impeller.
· Working environment: The working environment around vertical pumps is cleaner compared to that around horizontal pumps.
Shandong Dabo Pump Science and Technology Co., Ltd.
No.17 Nanhuan Rd, Boshan District,
Zibo, Shandong, China