ARTICLE
Jiangsu Teeyer Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd., Changzhou, Jiangsu, 213022, China
The application of MES System in the AAC industry
Illustration of a Digital Factory.
MES is a production information management system oriented towards the shopfloor execution layer of manufacturing enterprises. Its main functions include production planning management, real-time data collection, process monitoring, and resource optimization.
The American Advanced Manufacturing Research (AMR) organization defines MES as "a management information system located between the upper-level planning management system and the lower-level industrial control, facing the shopfloor layer." It provides operators/managers with plan execution, tracking, and the current status of all resources (people, equipment, materials, customer requirements, etc.).
Applying the MES system in the autoclaved aerated concrete production industry enables information management from sales orders through the production process to finished product warehousing, along with intelligent adjustment and operation of equipment. Through the collection, aggregation, and analysis of various data, it assists factories in transforming traditional management models into digital management models, achieving business datafication, work process standardization, and task visualization, thereby improving enterprise efficiency, enhancing competitiveness, and fostering sustainable development.
Development of MES
In November 1990, AMR proposed the concept of MES. In 1997, MESA proposed an MES functional component and integration model, including 11 functions, and stipulated that possessing one or several of these functions also qualifies as a single-function product within the MES series. In 2004, MESA proposed a collaborative MES architecture (c-MES).
In the early 1990s, China began tracking, researching, promoting, and piloting MES and ERP. Concepts with distinct Chinese characteristics were proposed, such as "Integration of Management and Control" and "Human, Financial, Material, Production, Supply, and Marketing," as seen in CIMS, MES, ERP, SCM, etc. However, development momentum was not rapid enough, potentially due to insufficient summarization, consolidation, promotion, persistence, refinement, or enhancement.
The earliest MES in China was introduced from Siemens in the early 1980s during the initial construction phase of Baosteel. China's industrial informatization has largely followed the path of Western industrialized countries, albeit half a step slower. Nearly all universities, industrial automation research institutions, and even national, provincial, and municipal government authorities began tracking and researching MES. From central to local governments, from learned societies to associations, from IT companies to manufacturing plants, from comprehensive websites to specialized portals, from comprehensive universities to specialized colleges, all were swept up in the MES wave.
MES is the link for enterprise CIMS information integration and a fundamental technical means for implementing agile manufacturing strategies and achieving agile shopfloor production. The factory MES is a production management technology and real-time information system for the shopfloor layer that has developed rapidly internationally over the past decade. MES can provide users with a rapidly responsive, flexible, and refined manufacturing environment, helping enterprises reduce costs, deliver on time, improve product quality, and enhance service quality. It is suitable for different industries (household appliances, automotive, semiconductor, communications, IT, pharmaceuticals) and can provide good enterprise information management for both single high-volume production and mixed-mode manufacturing enterprises that have both high-variety low-volume and high-volume production.
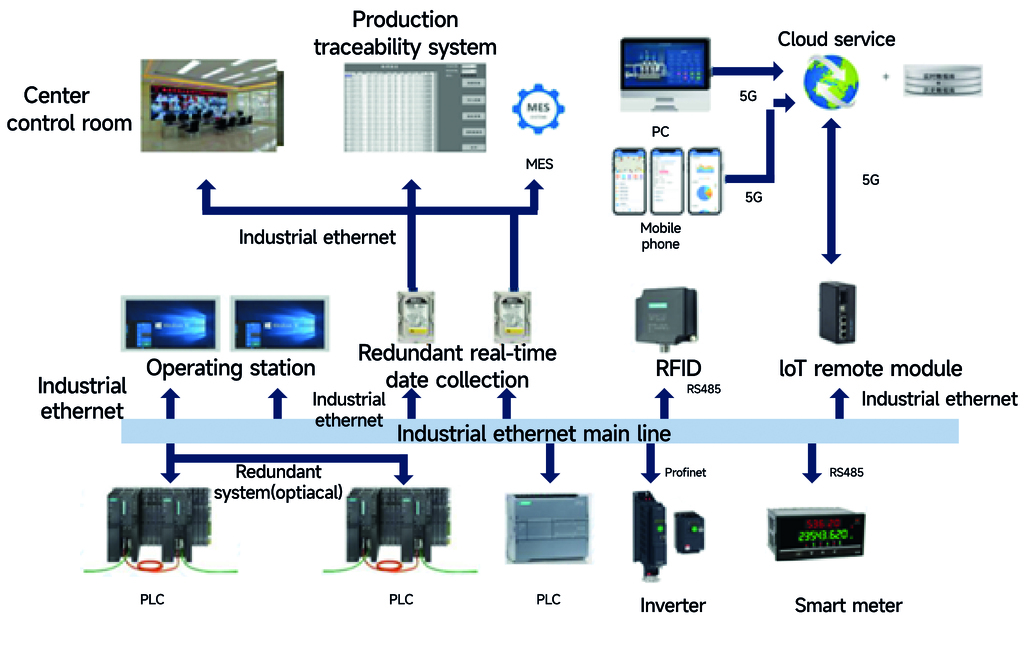
Deployment of MES
The MES system is widely used in various manufacturing and assembly industries. It can simultaneously provide real-time information services to production, quality inspection, equipment, process, logistics, warehouse, and planning departments. Through industrial Ethernet, it connects equipment control systems, barcode scanners, shopfloor PCs, large-screen display terminals, barcode printers, and network printers, enabling data communication.
Functions of MES
In the AAC enterprise MES system developed by Teeyer Intelligent, the functions of MES are divided into nine parts: Order and Plan Management, Warehouse and Logistics Management, Lean Production Management, Equipment Operation Management, Equipment Maintenance Management, Energy Consumption Management, Operational Exception Handling, System Integration Management, and Digital Twin System.
Order and Plan Management
Sales orders are formed by importing data associated through a CRM system or manually entered into the system. Within the system's order pool, products of different specifications, quantities, and delivery dates are gradually screened and matched based on priority rules, achieving batch production and intelligent mold allocation.
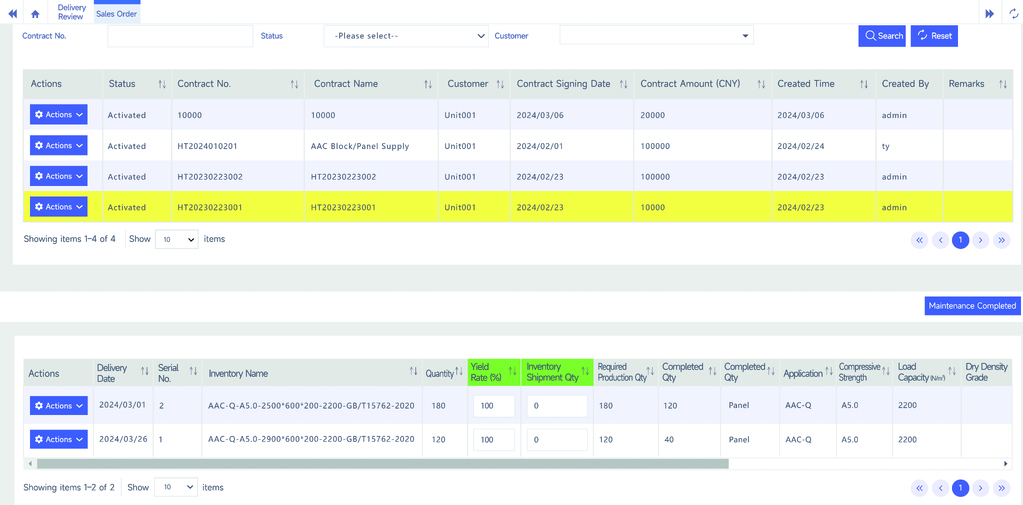
By screening product information such as delivery date, product bulk density, panel thickness, and panel length, intelligent combined mold production for similar specification products from different batches is achieved. This enhances the in-mold panel yield rate, reduces production batches, enables more detailed, efficient, and economical planned production, and schedules raw material supply and executes production based on the production plan.
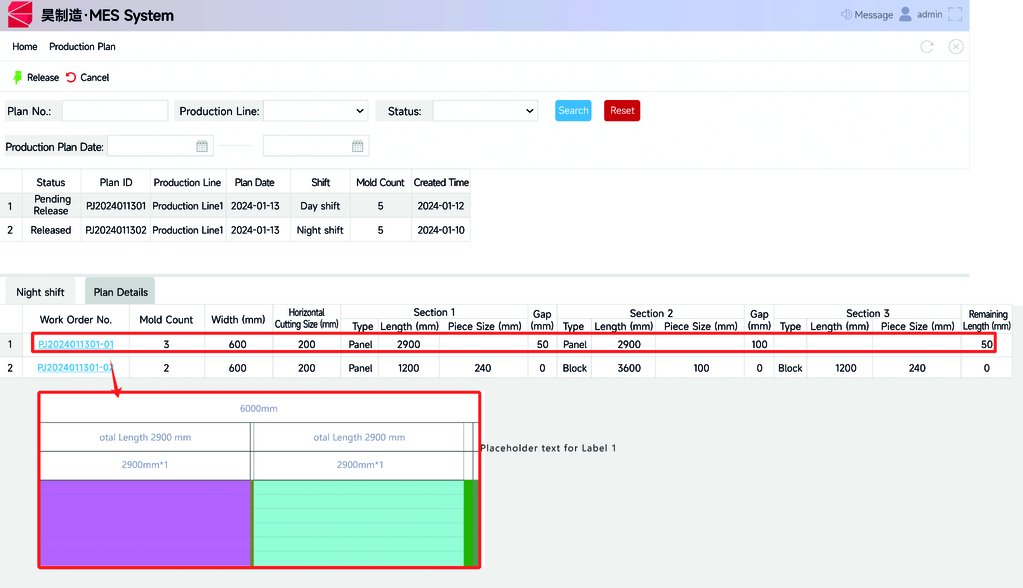
Warehouse and Logistics Management
Warehouse and logistics management includes functions for raw material and finished product storage management, inventory location monitoring, location alerts, consumption statistics, and inventory loss analysis.
Through integrated management of scales, silos, warehouses, and production lines, real-time inventory location monitoring is achieved. Online comparison of raw material incoming and outgoing stock is performed, inventory losses and consumption are promptly counted, and abnormal warnings are issued, enabling timely problem detection and rapid traceability.
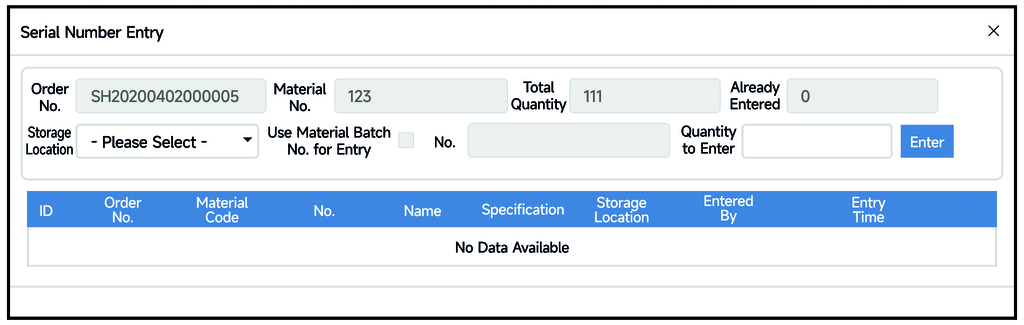
Through partitioned management of the finished product warehouse, electronic stack record-keeping, warehouse area radar monitoring, and scanning of incoming/outgoing vehicle information, real-time monitoring and control of finished product inventory and locations are achieved. Online comparison of product incoming/outgoing stock and inventory changes is performed, inventory losses and consumption are promptly counted, and abnormal warnings are issued, enabling timely handling of abnormal issues and rapid traceability.
Lean Production Management
Process management enables lean process control. Production plans are issued and monitored in real time. The process from raw material input to semi-finished and finished products is monitored in real time. The completion percentage and time for customer orders can be displayed promptly, achieving comprehensive control over the production process.
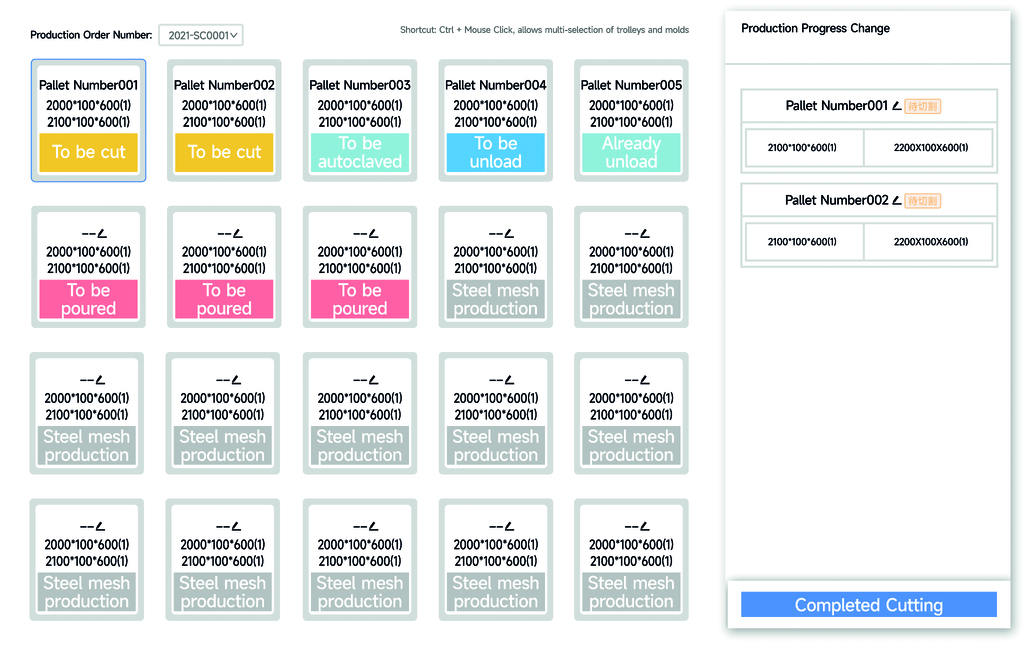
Through the application of RFID electronic tags, circulating items like moulds, side plates, and assembly frames have their own identifiers. The products they carry are accurately tracked via bundled electronic information. By reading RFID tags at various equipment operating stations, product information is automatically matched, facilitating quality tracking and traceability.
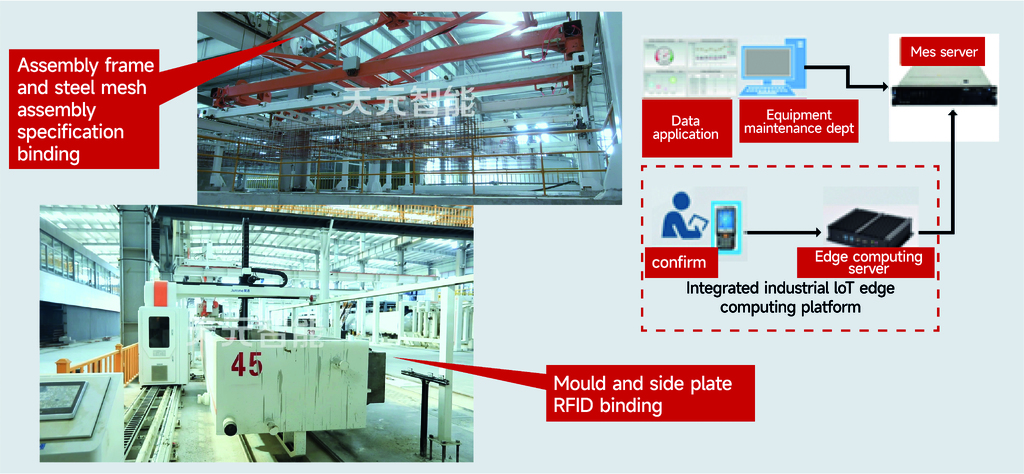
When products leave the autoclave, QR codes are printed or attached. These QR codes link the product batch, specification information, storage location information, customer information, construction location information, and manufacturing information stored in the server. This creates a unified code for product inbound/outbound logistics, logistics, and application. Relevant information can be obtained by scanning the QR code via WeChat (or similar application), facilitating customer application management.

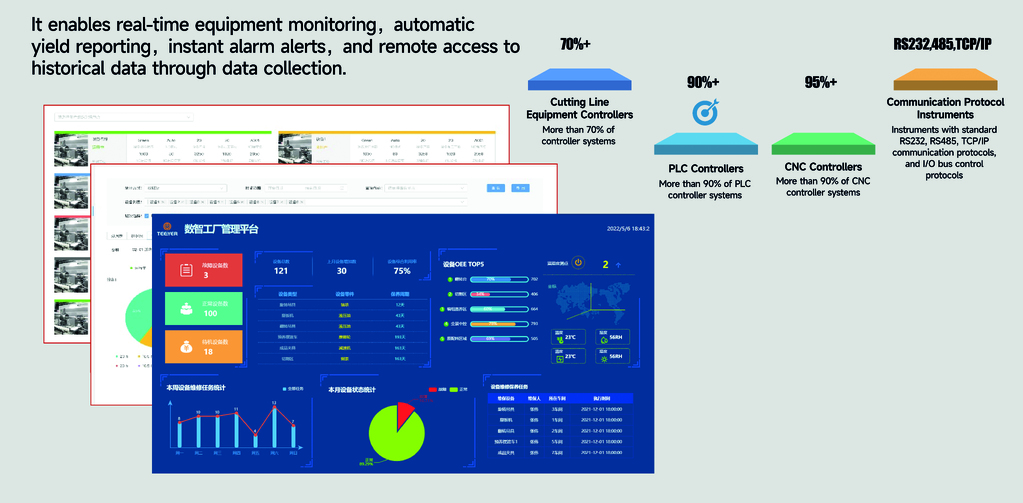
Equipment Operation Management
Various sensors monitor equipment operating parameters such as temperature, speed, pressure, flow, and current. The system judges equipment operating status in real time, intelligently analyzes equipment issues, facilitates timely equipment maintenance, and provides early warnings for maintenance needs, effectively ensuring equipment operation.
Energy Consumption Management
Monitors energy (water, electricity, gas) usage data of the production line, enabling energy itemization, automatic meter reading, and calculation of energy costs combined with production data. Provides weekly, monthly, and yearly dimensional reports, comprehensive query functions, including total usage of different energy types with year-on-year and month-on-month analysis, abnormal data analysis, and abnormal alarms. The energy consumption trend analysis page supports displaying daily trend changes for energy consumption in various areas of the entire line using bar charts and provides corresponding energy consumption optimization strategies.
Other Functions
Currently, the software for the above functional modules has been developed and put into use through offline testing. Online linkage and testing of equipment is progressing in an orderly manner. Other functions, such as CRM and ERP system integration, and the digital twin system module, are under development and refinement, and are expected to be released and deployed in the near future.
Future Prospects
Through the gradual improvement and refinement of the MES system, the production line will possess both batch manufacturing and flexible manufacturing capabilities. This will significantly reduce intermediate production control links, accelerate delivery schedules, reduce required positions and labor, save energy, and reduce consumption, realizing, to a certain extent, a "lights-out factory" or unmanned factory. Coupled with the future development of online monitoring systems for raw materials and finished products, the future fully automated factory will no longer be a dream.
Jiangsu TEEYER Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd, is located in National High-tech Development Zone in Changzhou City Jiangsu Province. It is a R&D and manufacturing enterprise specializing in complete sets of equipment and production lines for autoclaved aerated concrete machinery. The leading products include complete sets of AAC cutting equipment, AAC panel equipment and Engineering machinery.
TEEYER was established in 1989 with a registered capital of 160.7 million yuan, an area of 143,000 square meters, and over 400 employees. TEEYER has a provincial-level enterprise technology center with more than 80 R&D personnel. TEEYER conducts extensive industry-university-research cooperation, with no less than five research and development product projects and no less than 20 patents declared each year.
This Teeyer channel and all information presented here is provided by AAC Worldwide - the journal for the Autoclaved Aerated Concrete industry. All articles about Teeyer are available for free. Feel free to share information from this website with other industry professionals!
Jiangsu TEEYER Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd.
NO. 312, West Hehai Road, High Technology
Development Zone, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China
Postcode: 213125
T +86 13861131181
sales@teeyer.com
www.teeyer-global.com